-
-
April 1
One-day boycott against Jewish businesses.
-
-
-
April 7
Law for the Reestablishment of the Professional Civil Service removes Jews from the civil service and bans Jewish teachers from public schools.
-
-
-
April 7
Law on the Admission to the Legal Profession forbids the admission of Jews to the bar.
-
-
April 25
Law against the Overcrowding of German Schools and Universities limits registration of Jewish students to 1.5% of total registration.
-
September 22
Non-Aryans are banned from positions of influence in the arts, literature, music, theatre, broadcasting and the press.
-
September 1
Jews are forbidden to own farms.
-
May 21
Army Law expels Jewish officers from the army
-
-
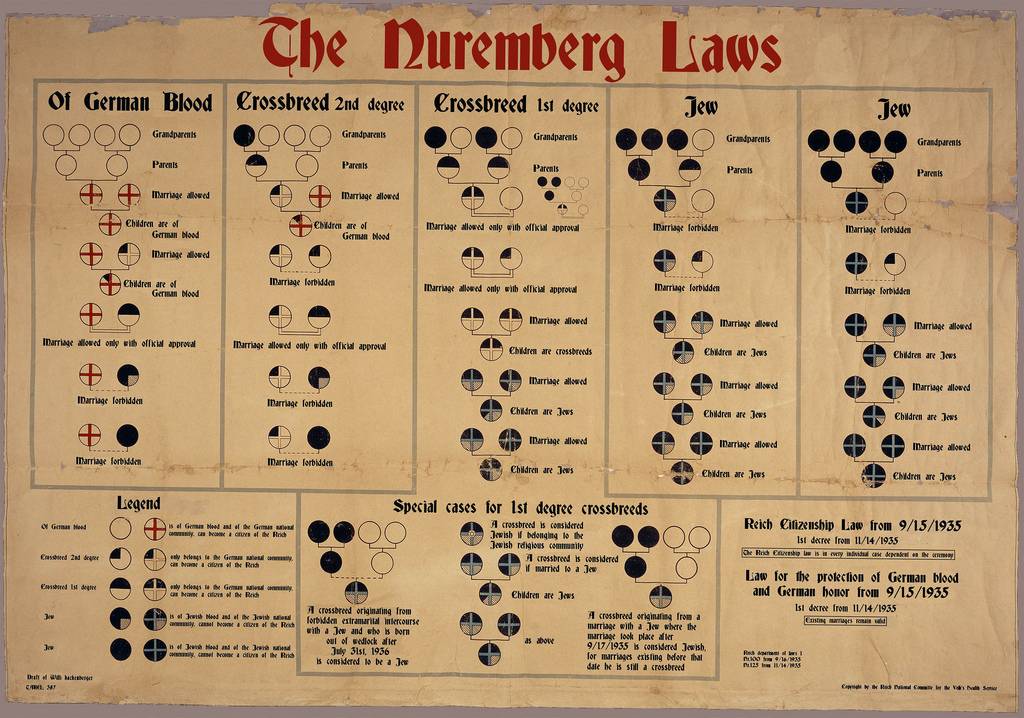
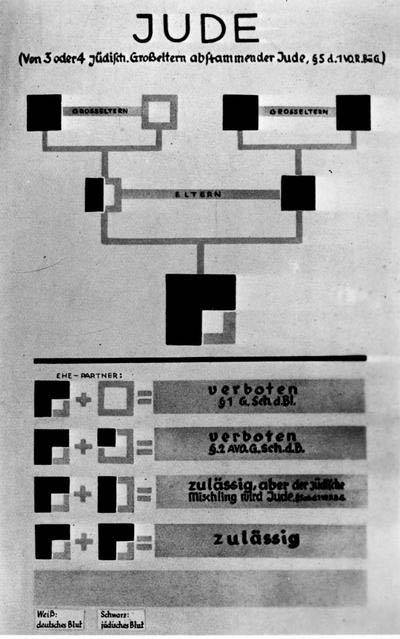
September 15
The Law for the Protection of German Blood and Honour and the German Citizenship laws are passed. Known as the “Nuremberg Laws”, they prohibit marriage and sexual relationships between Germans and Jews and state that only persons of “German or related blood” can be citizens.
-
-
January 11
Executive Order on the Reich Tax Law forbids Jews to serve as tax-consultants.
-
April 3
Reich Veterinarians Law expels Jews from the veterinary profession.
-
April 9
The Mayor of Berlin orders public schools not to admit Jewish children until further notice.
-
June 11
Jews are prohibited from giving testimony in courts of law.
-
January 5
Law on the Alteration of Family and Personal Names forbids Jews from changing their names.
-
February 5
Law on the Profession of Auctioneer excludes Jews from this occupation.
-
March 18
The Gun Law excludes Jewish gun merchants.
-
March 30
The Law Concerning the Legal Status of the Jewish Religious Communities removes the status of “corporations under public law” from Jewish religious organizations, thereby removing state support and protection.
-
April 22
Decree against the Camouflage of Jewish Firms forbids changing the names of Jewish-owned businesses.
-
-
April 26
Nazis force Jews to register their assets, a first step toward total exclusion from the German economy. The Order for the Disclosure of Jewish Assets requires Jews to report all property in excess of 5,000 Reich marks.
-
-
July 11
Reich Ministry of the Interior bans Jews from health spas.
-
-
July 25
Jewish doctors are forbidden to treat ‘Aryan’ patients.
-
-
-
August 17
Any Jew whose name does not immediately identify him or her as Jewish required to add name “Israel” or “Sarah” to passports and identity papers. The Nazi government drew a list of recognizable Jewish names to define who needed to change names.
-
-
September 1
Jewish lawyers are forbidden to have “Aryan” clients.
-
-
October 5
Following a request from Switzerland, passports of German Jews are marked with “J” for Jude (Jew). Jews must surrender their old passports, which will become valid only after the letter “J” had been stamped on them.
-
-
November 12
Decree on the Exclusion of Jews from German Economic Life closes all Jewish-owned businesses.
-
November 15
Reich Ministry of Education expels all Jewish children from public schools.
-
November 28
Reich Ministry of Interior restricts the freedom of movement of Jews.
-
November 29
Reich Interior Ministry forbids Jews to keep carrier pigeons.
-
December 14
Executive Order on the Law on the Organization of National Work cancels all state contracts held with Jewish-owned firms.
-
December 21
Law on Midwives bans all Jews from the occupation.
-
August 1
The President of the German Lottery forbids the sale of lottery tickets to Jews.